- Cloud storage manager
- OpenStack Swift on Mac: Everything you need to know
OpenStack Swift on Mac: Everything you need to know
The Object Storage module aka Swift project of the OpenStack complex is designed to organize long-term storage of unstructured data in the cloud. Being a difficult topic, Mac users search for information that can help them in understanding. In our article, we have covered the answers to OpenStack Swift architecture, and requirements as well as given tips about alternative ways of working with the cloud.
What is OpenStack?
OpenStack is a project launched by NASA and Rackspace in 2010 and is the fastest-growing open-source project. Its mission is to create a cloud computing platform useful for both public and private implementations. The product consists of free software distributed under the Apache license. The two main principles are simplicity and scalability.
OpenStack has many sub-projects under its umbrella ranging from computing and storage all the way to networking, including other applications. The object storage project is called OpenStack Swift and it is highly available, distributed, without dedicated management, and has a software stack that brings the system eventually to data consistency.
The main features of storage based on the Swift module are relatively low speed of writing/reading data and staticity (working with data only as with integral objects), and inability to use for the organization of a full-fledged, dynamic file system. Making adjustments to the data (even minimal ones) of any object in the storage is possible only by complete replacement (overwriting) of the object.
In order to access files stored in OpenStack Object Storage Swift, a Command-line should be used, as there is no native client. However, as the latter does not have a user-friendly interface and lots of users are afraid of it, it is a good idea to resort to cloud manager apps that can help you work with clouds.

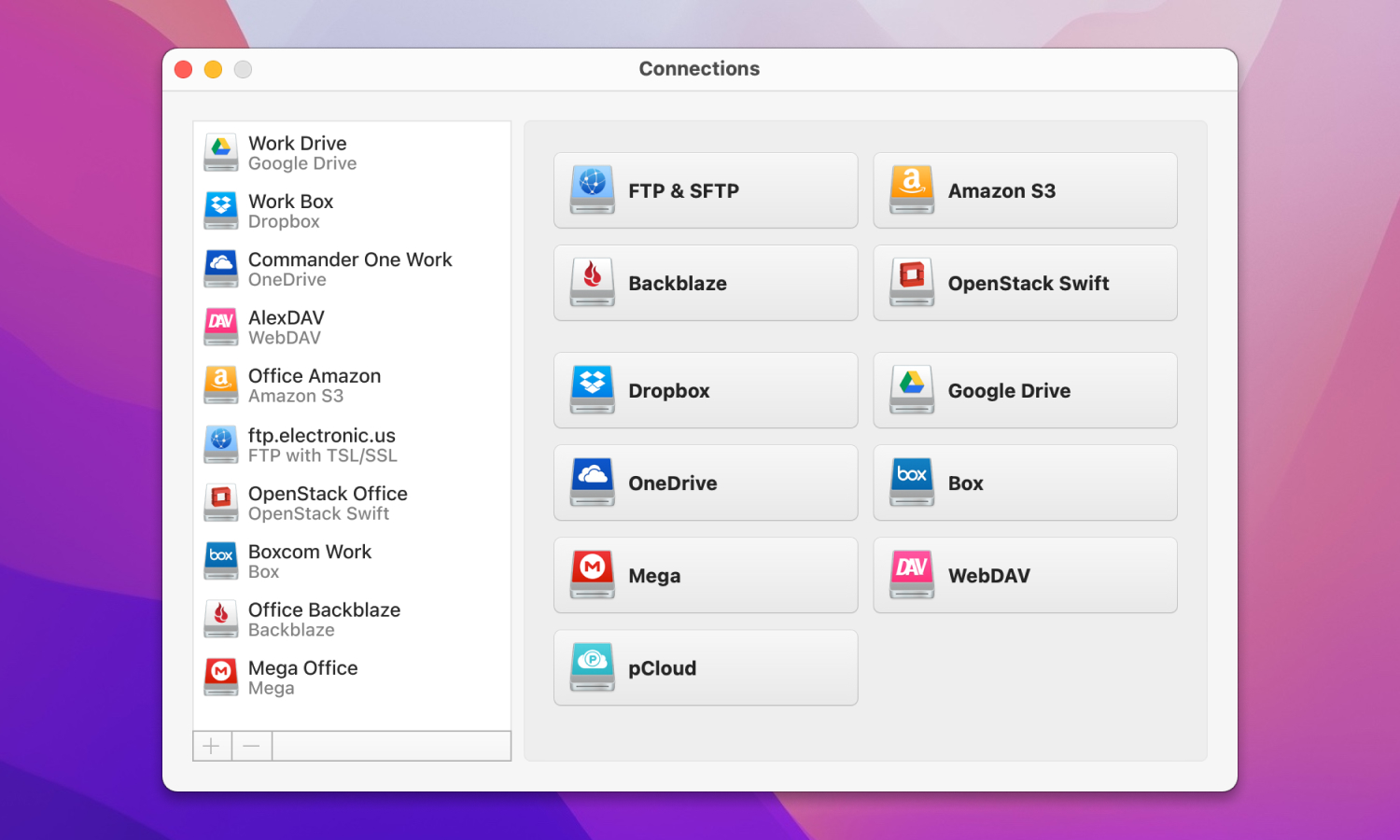
Alternative Way to Work with Cloud Storage Services — CloudMounter
CloudMounter is an excellent choice if you have to work with data stored on different clouds. The app works with almost all cloud storage services, including, Google Drive, Amazon S3, Dropbox, Mega, MS OneDrive, and OpenStack Swift, as well as FTP, SFTP, and FTPS remote servers. The app allows you to have flawless management of all the data stored online right from Finder or File Explorer.
Being a reliable cloud manager, CloudMounter support work with multiple cloud accounts at once, allowing you to transfer files not only within one cloud storage but also to other supported cloud storage services. The only thing that is required is to map them as network drives by following simple instructions.
Additionally, this cloud manager offers an AES-256 encryption algorithm to ensure extra protection and minimize the risk of keeping your data online.
How to Mount OpenStack Swift as a Drive with CloudMounter
Mounting OpenStack Object Storage Swift as a network drive won’t take much time. Just by following this simple guide, you will be able to access it whenever you need.
1. Download and install CloudMounter on your Mac computer.
2. Launch the app and select OpenStack cloud storage from the new connection window.
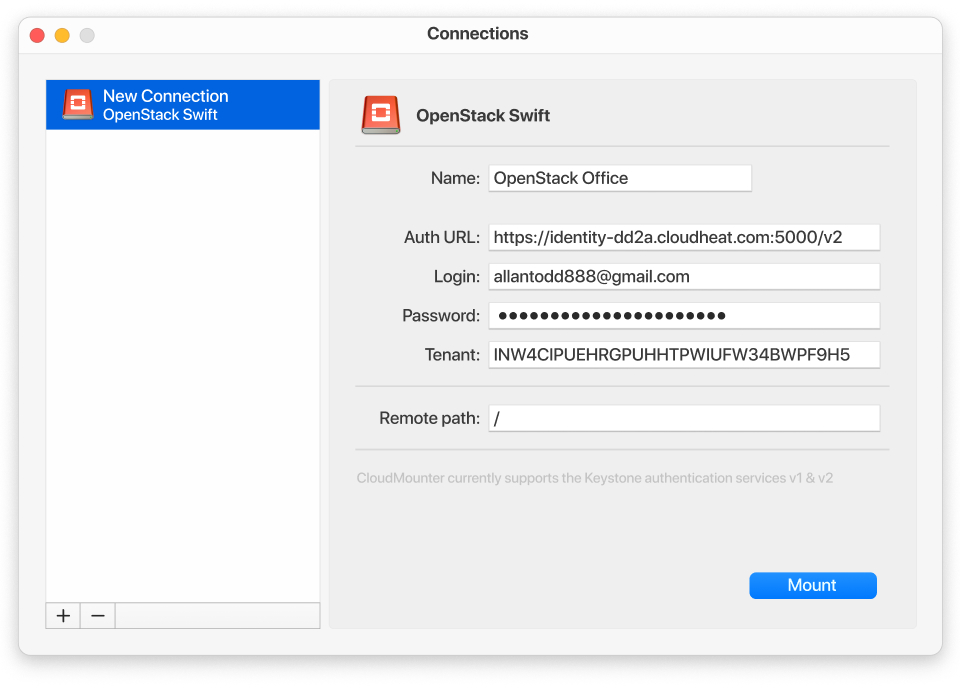
3. After that you will be asked to provide the corresponding information:
- name;
- authentication URL;
- login;
- password;
- tenant (aka “project”);
- remote path.
4. Click the “Mount” button to establish the connection to Finder on your Mac.
P.S. CloudMounter is currently compatible with Keystone authentication services v1 and v2.
How OpenStack Swift Works
OpenStack Object Storage Swift provides a scalable redundant distributed object storage that uses clusters of standardized servers. By “distributed” it is meant that each piece of data is replicated across a cluster of storage nodes. The number of replicas is configurable but must be at least three for commercial infrastructures.
Access to objects in OpenStack Swift is carried out through the REST interface. These objects can be stored, retrieved, or updated on demand. Object storage can be easily distributed across a large number of servers.
OpenStack Swift uses a completely different architecture from traditional enterprise storage systems with a distributed architecture built on public servers. OpenStack Swift architecture includes four main components:
- Proxy Server that brings all the components of the system together.
- Object Server that is responsible for data storage.
- Container Server is responsible for returning a list of objects.
- Account Server that provides container listings for a specific account.
In addition, another machine called a proxy server exposes the OpenStack Swift API to users and performs the transfer of objects from and to clients on request.
A typical OpenStack Swift infrastructure is a cluster, where one of the machines acts as a proxy, a few machines act as container and account servers, and the rest (hundreds or thousands of machines) are container servers. The proxy server exposes the OpenStack Swift API to users and performs the transfer of objects from and to clients on request.
Rings are used by the proxy server to find the real position of the data in the cluster. This is a kind of database that describes the location of the data. Each time new data is written to the storage, deleted, or nodes fail, it is modified. Separate rings are provided for accounts, containers, and objects.
The most crucial component of a Swift OpenStack cluster is the object servers. Their main function is to store and return data. Any storage objects eventually end up on the hard drives of these servers, which write data to regular files, accompanied by metadata written to the extended file attributes.
Reliability of data storage is achieved by duplicating to several servers at once so that if one of them fails, the system will be able to restore data from another server and duplicate them again. The system creates three copies of each object by default, so machines that do not even have RAID controllers can be used as the iron part of the cluster.
Transparent scalability is one of the main advantages of the system. To expand the storage, you just need to connect a new node to the cluster, and OpenStack Swift will take care of the rest of the work of synchronizing it with the storage. This cluster is best suited for storing data such as virtual machine images (in fact, this is what it was created for), photo banks, emails, backups, etc.
The OpenStack architecture is quite fragmented. There are a very large number of "moving parts", the relationship between which is not always absolutely clear. In an effort to make it simple for the end user, developers ended up making it too complicated. Any configuration to suit the needs of the user turns it into a nightmare. In general, after fighting with OpenStack for quite a long time, I abandoned it and switched to another cloud.— Our expert's opinion
Use Cases for OpenStack Swift
Storage for cloud applications
OpenStack Swift is suitable for cloud apps that require scalable and distributed storage solutions. It allows developers to cost-effectively store large amounts of unstructured data such as images, videos, and backups.
Backup and archiving solutions
OpenStack Swift provides a reliable solution for storing large amounts of data for long periods of time. Organizations can use Swift to back up important data, ensuring it is protected from loss or corruption.
Collaboration Workspaces
OpenStack Swift facilitates team collaboration by allowing multiple users to access and edit files simultaneously. This is great for projects where team members in different locations need to work together on documents or other digital content.
Storing and analyzing big data
Swift’s capacity to handle large-scale data workloads without sacrificing performance is critical for big data applications.
Content Delivery Networks (CDNs)
OpenStack Swift can be used as an original storage source for CDNs. By storing content in Swift, organizations can ensure that their data is distributed across multiple regions, improving speed and reliability of access for end users.
Conclusion
OpenStack is a set of free software projects that can be used to create computing clouds and cloud storage, both public and private (working only for the internal needs of the company). OpenStack has the advantages that are typical for open source projects, it is possible to create your own software solutions for organizing the cloud on its basis. To facilitate work with OpenStack object storage Swift it is recommended to use cloud managers that allow transferring files right from Finder.
Frequently Asked Questions
Swift has a limit on the size of a single loadable object to 5 GB. However, the size of a loaded object is virtually unlimited due to the concept of segmentation.
To access your OpenStack instance, follow these steps:
- Go into your instances’ details page.
- Select the project and then go to Compute > Instances.
- Open the console.
- Login to the Instance using your account.
Swift or Object Storage is conceptually similar to Amazon S3, however, Swift has strong scalability, redundancy, and persistence, and is compatible with the S3 API. Cinder provides block storage similar to Amazon’s EBS storage service currently mounts for virtual machines.
You can access OpenStack Swift from the command line. However, it is rather convenient to use third-party cloud manager apps.