Will Cloud Gaming on 5G result in a difference with desktop gaming?
Cloud gaming enables users to stream game content to compatible computers or mobile devices. A prerequisite to viable cloud gaming is a reliable and high-speed Internet connection. One of the major selling points of cloud gaming is eliminating the need for expensive gaming consoles or dedicated computers. Users access a high-powered cloud gaming server over the Internet and play on their personal computers or mobile devices.
The convergence of 5G and cloud gaming promises to provide gamers with a new method of enjoying low latency streaming while playing their favorite game. This article looks at how 5G for cloud gaming will change the landscape for gamers.
The latency problems affecting cloud gaming
A major factor impeding the ability to fully enjoy cloud gaming is latency. Latency is the amount of time it takes data to go from one point to another over a network. Latency is usually measured between a client, or user device, and a server residing in a remote data center. The length of time it takes for a server to respond to a request made from a remote PC is latency and is a measurable quantity. Speaking about cloud gaming latency, the term “latency” refers to the time lapse between a user’s actions and the corresponding response of the game.
Factors that define latency:
• Network factors include the distance between the two devices engaged in communication, in this case, a cloud gaming server and a gamer’s client device. As the distance increases, so too does the amount of latency. Another factor is the number of networks data must traverse from start to finish. Moving across multiple networks increases the potential for additional latency.
• Latency is also affected by issues on the server. Optimizing images, minimizing code, and using a content delivery network (CDN) can all be used to help control latency.
• There may be issues on the client side that contribute to latency. Using Ethernet rather than WiFi can reduce latency, as can obtaining additional bandwidth. Users should also ensure that all firmware upgrades are installed on their home networking components.
Everyone who has ever used a computer has been affected by latency. It can be very frustrating waiting for delayed responses from a website. Too much latency and lag can result in potential customers abandoning a site in favor of one that is more responsive.
In the worlds of cloud gaming and the more competitive esports, latency can be much more than occasionally annoying. An increase in latency of even a few milliseconds can make the difference between a playable and unplayable game. Gamers cannot enjoy playing cloud games on a remote desktop when their controller input lags due to high latency.
In esports, where there is serious money involved, the problem becomes even more important to solve. Players cannot compete fairly if they are handicapped due to latency and network problems. The hope is that 5G cloud gaming will eliminate most of these latency issues.
Current and projected 5G adoption
5G is the fifth generation of wireless, cellular technology. On a 5G network, data can be sent over wireless broadband connections at multi-gigabit speeds. Some estimates expect 5G networks to reach peak speeds of 20 gigabits per second (Gbps). These speeds can provide a latency of 1 millisecond or less, essentially paving the way for real-time communication and feedback.
The key factor holding up the use of 5G for cloud gaming or any other purpose is the lack of infrastructure necessary to provide connectivity to the high-speed network. 5G signals use large numbers of small cells placed strategically on structures such as streetlights and building roofs. The millimeter wave spectrum which is used to transmit data over 5G can only travel over short distances and can be interfered with by weather conditions or physical objects like walls and trees.
These constraints mean that large capital investment is required to implement a robust 5G network in any particular area. Wireless carriers around the world are addressing this issue at widely varying speeds, making 5G more readily available in certain geographic locations.
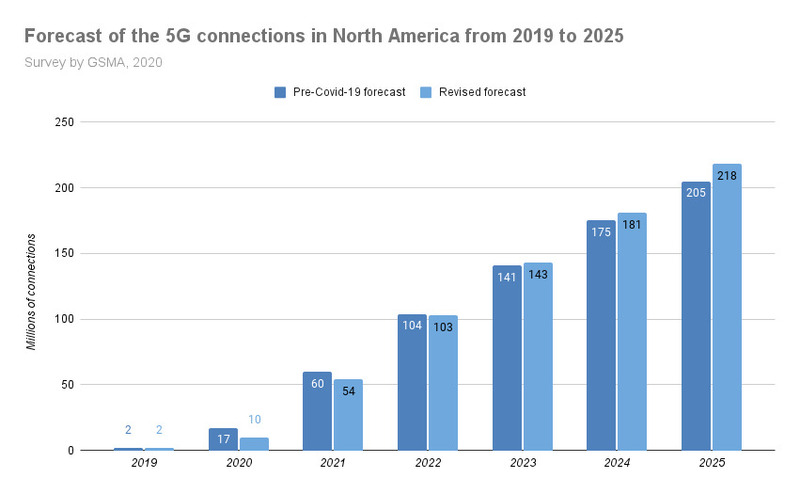
The adoption of 5G technology has been impacted by the effects of the COVID-19 pandemic. An excellent example of this phenomenon can be seen in the accompanying chart from The Mobile Economy North America 2020 report by GSMA, page 14. It illustrates how the rollout of 5G has been impacted by the virus. A slowdown in 2020-2022 is expected to be followed by a period of more rapid growth as companies look to bring 5G to the masses.
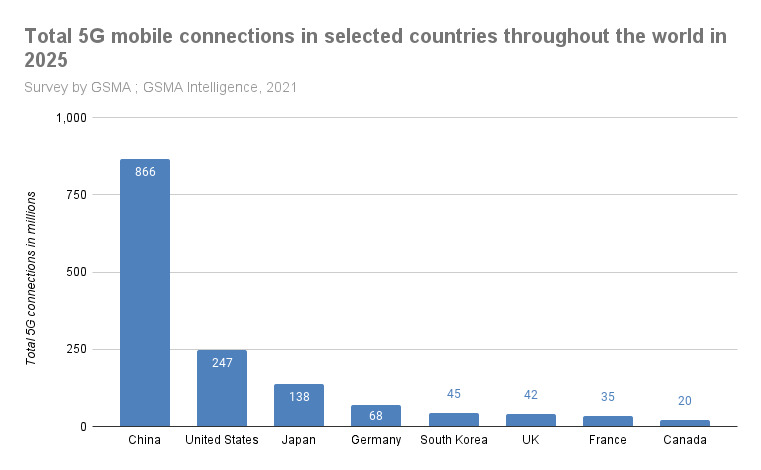
The number of 5G network connections is expected to vary widely by 2025 as can be seen in the similar report from 2021, page 11. China is projected to lead the world with 866 million 5G connections. The U.S. is a distant second with an estimated 247 million 5G connections. South Korea will have the highest density of 5G connections per population size.
The availability of 5G networks to the gaming community promises to increase the interest in cloud gaming. The combination of cloud gaming and 5G will drive new trends and offerings by game developers and content providers. Gamers can expect companies to offer more extensive game libraries and supply consumers with a constant stream of new titles.
Cloud gaming popularity and trends
The concept of cloud gaming has been around for years. Trends in computing, networks, and consumer sentiment are all contributing to greater acceptance for the industry.
Factors that influence cloud gaming demand:
• Faster and more consistent network connectivity has enabled gamers to access cloud gaming servers with reduced latency. The emergence of 5G networks will only make the cloud gaming experience better for anyone within the range of a signal.
• Consumers are becoming accustomed to using streaming services for entertainment and news. Many people choose to watch Netflix or Amazon Video over the offerings of their cable TV provider. The acceptance of streaming options bodes well for the cloud gaming industry.
• Mobile devices are now equipped with the capabilities to carry the high-definition video necessary for cloud gaming. Additionally, consumers are getting used to the concept of watching, or in this case playing games, on a wide variety of devices including TVs, computers, smartphones, and tablets.
As the desire for cloud gaming increases, so does the number of providers offering content to their subscribers.
Top cloud game services currently available:
• Xbox Game Pass – This service features a rotating selection of over 100 games that can be streamed and played on an Xbox, Windows 10 computer, or Android device.
• Vortex – A Vortex subscription gives you access to a large gaming library that can run on PC, Mac, and Android devices. It features built-in browser support and lag-free streaming at 60 frames per second.
• Amazon Luna – With Amazon Luna you get multiple channels for game streaming and variable subscription plans. A dedicated Luna controller is available to improve gaming performance and the service features games compatible with PC, Mac, Android, and iOD devices.
• PlayStation Now – This service brings the library of PlayStation titles to cloud gamers with your subscription. Currently, you can only play games on a PlayStation console or a Windows PC as there is no support for mobile devices.
• Google Stadia – Using Google Stadia, subscribed users can play free games every month and can also purchase games through the service. These games reside in the Stadia cloud and can’t be downloaded to your device.
True 5G cloud gaming provides higher connectivity speed and reduced lag. While all cloud gaming services can be accessed using slower networks, playing on a 5G network will demonstrate the real potential of gaming in the cloud.
Conclusion
So how does 5G help cloud gaming? Simply put, by eliminating the lag and latency that accompanies streaming gaming content, cloud gaming on 5G becomes a much more pleasant and satisfying experience. Gamers will be able to enjoy their games without an expensive gaming console or a computer outfitted with an expensive video card. All they will need is a 5G connection and a device compatible with the gaming service they choose.
While the future of 5G cloud gaming is promising, it may be some time before everyone who wants 5G can get it. Currently, due to inconsistent infrastructure implementation, most 5G connectivity is confined to major metropolitan areas. It might be several years before 5G networks are available everywhere.
If you are a gamer lucky enough to be in an area with cloud gaming on 5G availability, you might want to rethink your prospective purchase of a new gaming console or screamingly fast desktop computer. Before making that commitment, investigate the offerings of cloud gaming providers to see if they appeal to you. If so, you can get started with a trial membership to test your equipment and see if the promise of 5G cloud gaming lives up to reality. You may find that there is a new and exciting alternative to your legacy gaming systems waiting for you.

