Top 5 New Security and Privacy Features Released in macOS Sequoia
With the introduction of the new macOS Sequoia, Apple introduced many improvements. The operating system comes with added pops of color and user-friendliness, as well as enhanced security and privacy. There are over 70 security fixes to address different vulnerabilities. Let’s dive into the most prominent new features of the latest macOS.
New Passwords App
The new app changes how password management is handled across the Apple ecosystem. Previously, this capability was split between Safari and System Preferences. Now, however, Apple’s solution is more akin to a traditional password manager. It allows users to store all their passwords, passkeys, and other credentials in one place, organizing them in folders or groups. The AutoFill feature will still automatically complete your passwords on websites or suggest strong passwords when creating new accounts. Thanks to synchronization across devices, passwords can be accessed from Mac, iPhone, iPad, and even Windows via the iCloud for Windows app. The app is backed by end-to-end encryption.
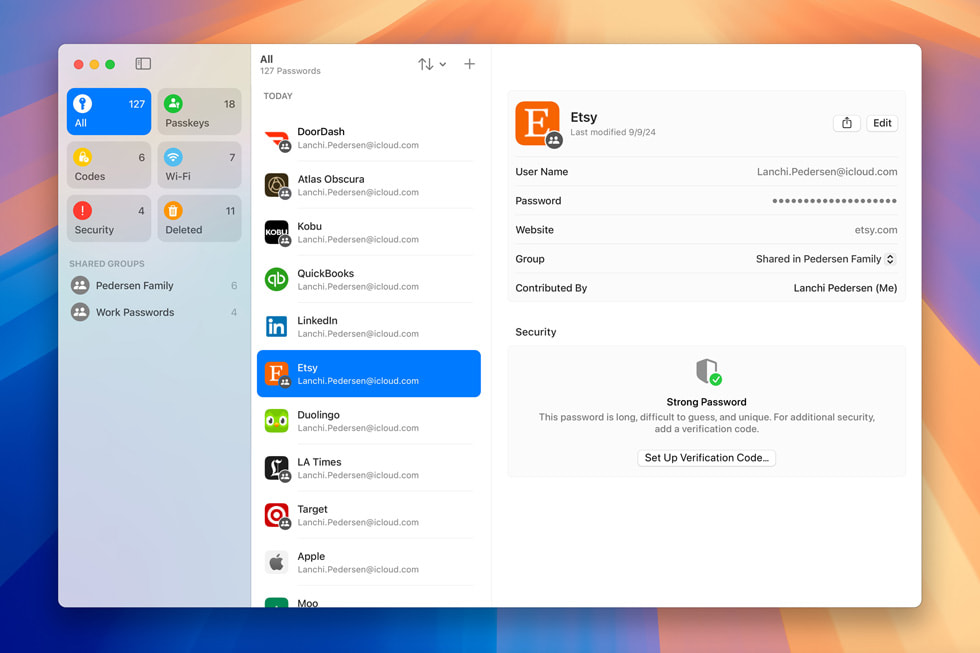
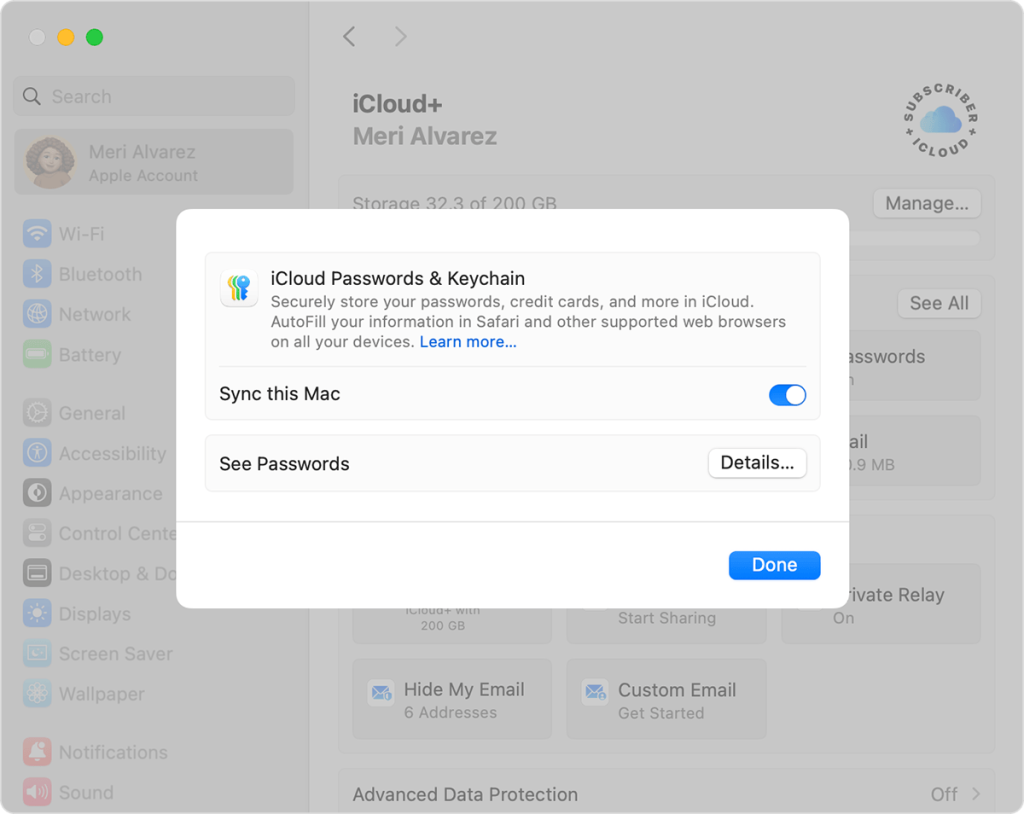
iCloud Keychain
The iCloud Keychain technology is still in place. The Passwords app now acts as a gateway to Keychain, making it easier and even more user-friendly to store, search, edit, and retrieve passwords across all of their Apple devices.
Rotate Wi-Fi Address Option
With macOS 15 Sequoia, Apple presents a new privacy feature called Rotate Wi-Fi Address. Designed to serve as a defense mechanism against tracking, it changes your device’s MAC address over time. Previously, your computer would get a separate MAC address for each Wi-Fi network it connected to. Now, the address will change about every 2 weeks. This way, your address will no longer appear the same to other devices and people on the same network as you, preventing third parties from creating a profile based on your network behavior. The new feature is available in the settings of any Wi-Fi network and replaces Apple’s former Private Wi-Fi Address option.
Changes to Gatekeeper
Gatekeeper is a built-in feature in macOS that protects you from malicious software. It does so by scanning all apps not downloaded from the App Store and issuing warnings about any security issues it encounters. Previously, users could use Control-click to override Gatekeeper when opening non-signed or notarized Mac apps. In macOS Sequoia, Gatekeeper is more difficult to bypass, requiring users to go to System Settings > Privacy & Security to review security information and approve using their admin password. The purpose of this mechanism is to safeguard users from malware distributed outside of the Mac App Store and to encourage them to focus on downloading software from official sources.
Private Cloud Compute
The new Private Cloud Compute (PCC) technology sets a new standard for privacy in artificial intelligence. It allows Apple to scale its computational power: if a request is too large to process locally, your device will not only use on-device processing but also larger external servers when needed. At the same time, it ensures privacy protection is in place. The servers, powered by Apple silicon chips, are more secure than traditional ones. Independent security experts can verify these servers and Apple devices can only communicate with them if they have been publicly logged for inspection.
According to Apple, PCC does not store user data. Once a task is completed, all data and logs are immediately deleted. It will not be used to train AI models.
To Sum Up
The launch of macOS Sequoia has brought about several privacy improvements. The new Passwords App, together with iCloud Keychain, helps users keep all their passwords and other login credentials safe and easily accessible. Rotate Wi-Fi Address works to prevent tracking when using Wi-Fi networks, while Gatekeeper now works harder to protect from malicious software. Last but not least, Private Cloud Compute harnesses the power of AI, making it safer for Apple devices to combine on-device computing and external servers.
These are some of the features introduced with Apple’s new Mac operating system that we believe are the most noteworthy and have been described in our article dedicated to privacy and security in macOS Sequoia.
